============================================================================
There are 4 network types:
External
LAN
HotLAN
DMZ
Communication between networks is routed according to this table:
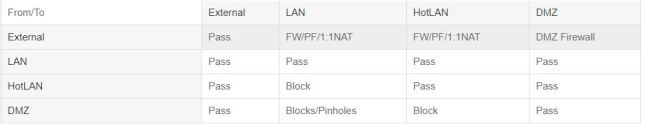
External
External is simply an interface that is Internet facing. External does not mean WAN in ClearOS as an external interface can exist on a LAN network. For example, if you have a Standalone ClearOS server (ie. not acting as the gateway), External is the role you would select even though it is on the LAN. External networks are the only role with a gateway address specified. The ‘Network Mode’ affects how the External role is deployed. The modes are:
1.Gateway
2.Standalone
3.Standalone – No Firewall
4.Trusted Gateway (hidden mode
1. Gateway
Under gateway mode the firewall is active on the External interface. Additionally, networks behind the firewall are routed (DMZ, HotLAN, LAN) and NAT is applied to LAN type networks (LAN, HotLAN).
2. Standalone:
Under Standalone, the External interface is firewalled. This is useful if you are running ClearOS as a server in the cloud.
3. Standalone – No Firewall:
Under this mode, the External interface is not fire-walled. This is useful if you are running ClearOS as a server on a local network.
4. Trusted Gateway:
Trusted gateway is a hidden, unsupported mode that does not have a firewall on the external interface. It is useful for LAN routing and transparent bridging.
LAN
Interfaces designated as LAN have NAT applied to them as well as have access to all networks. Specify LAN for networks that should be able to access all networks.
HotLAN
Interfaces designated as HotLAN have NAT applied to them but do not have access to LAN networks. Specify HotLAN for networks that are considered restricted but still need access to the Internet.
DMZ
Interface designated as DMZ are designed for public IP networks that are directed to the ClearOS server as the gateway. This allows you to specify public IP addresses and have firewalling. Hosts behind the DMZ can ONLY access LAN addresses where pinholes are opened between the DMZ network and the LAN. NAT is NOT applied to DMZ hosts.